Graphs
Write a program that implements Breadth-First and Depth-First Search.
Background
A graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of some number of nodes connected by edges. Edges can be directed (one-way) or undirected (two-way).
Graphs can be used to represent a wide variety of data structures - any time there is a relationship between different data points, a graph may be useful. Mazes, social relationships, networks, maps, etc. - the possibilities are many.
In order to either find a particular node (“search”) or find a particular path between nodes (“path-finding”), the graph must be traversed, or explored.
In the lecture and slides on the topic (see Schoology to review), we discussed two types of graph traversal: Breadth-First Search and Depth-First Search, commonly abbreviated as BFS and DFS.
For example, consider the following graph:
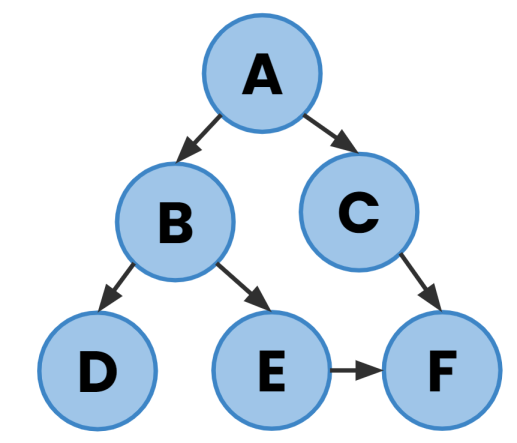
Note that since this is a directed graph, the connections are one-way and there is no path back from the bottom-most nodes.
Starting at node A and using DFS, the nodes would be visited in this order:
A → B → D → E → F → C
While using BFS, the order would be:
A → B → C → D → E → F
Implementing graphs in Python
In Python, we can represent a graph using a dictionary. For example, to represent the graph above, we could use the following code:
graph = {
"A": ["B", "C"],
"B": ["D", "E"],
"C": ["F"],
"D": [],
"E": ["F"],
"F": []
}
Each node is a key in the dictionary, and its value is a list of the connections. Traversing the graph means retrieving a node’s list of neighbors. For example, to loop through the nodes connected to “A”:
for neighbor in graph["A"]:
print(neighbor)
# Prints "B" and "C"
Implementation
You will write a program, graphs.py that will implement both DFS and BFS searches. First, your program’s command line will accept two arguments: the type of search to perform, and filename containing the graph data.
Your program will do the following:
- Check that the command-line input is valid.
- Read the data from the file into a dictionary called
graph. The data will be in text format, with each line of the file representing one node and its connections. For example, the text file for the graph above would look like this:
A,B,C
B,D,E
C,F
D
E,F
F
- Be sure to check that
sys.argv[2]is either"bfs"or"dfs". If not, display an error and exit. - Write two functions:
bfs()anddfs()that traversegraphand print the nodes in the order visited.
The output of your program should look like this:
$ python graph_search.py graph.txt dfs
A B D E F C
Make sure your program works with any graph, not just the example one above. Here are two more you should test with:
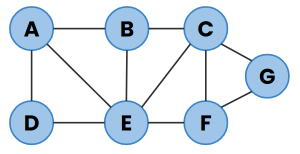
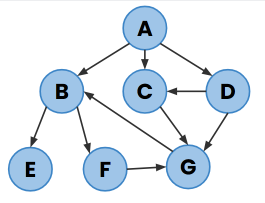
Checking your code
Execute the below to evaluate the correctness of your code using check50.
check50 scienceacademy/problems/2025ap/graphs
How to Submit
submit50 scienceacademy/problems/2025ap/graphs